יועץ סביבתי בפרויקט – יתרונות מרכזיים
16 בSeptember 2018
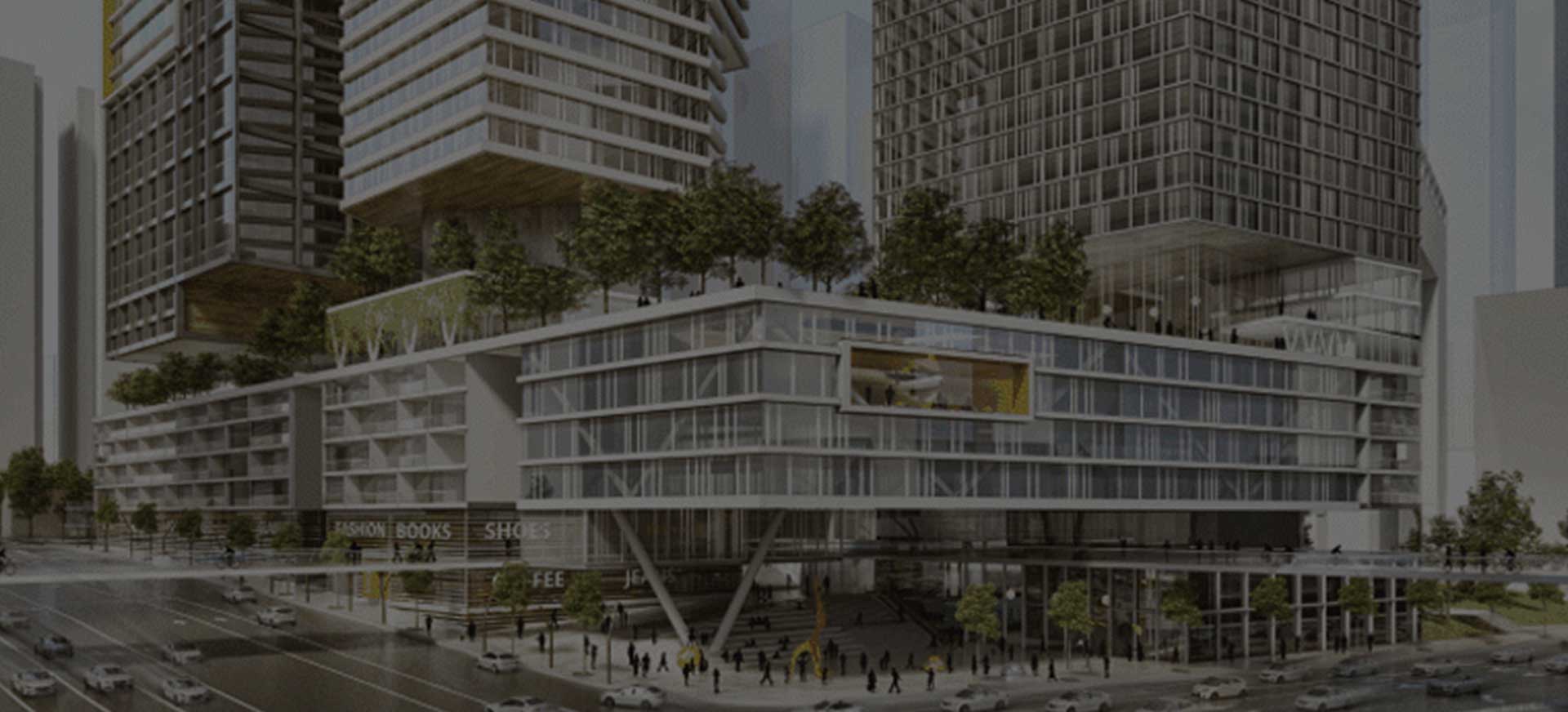
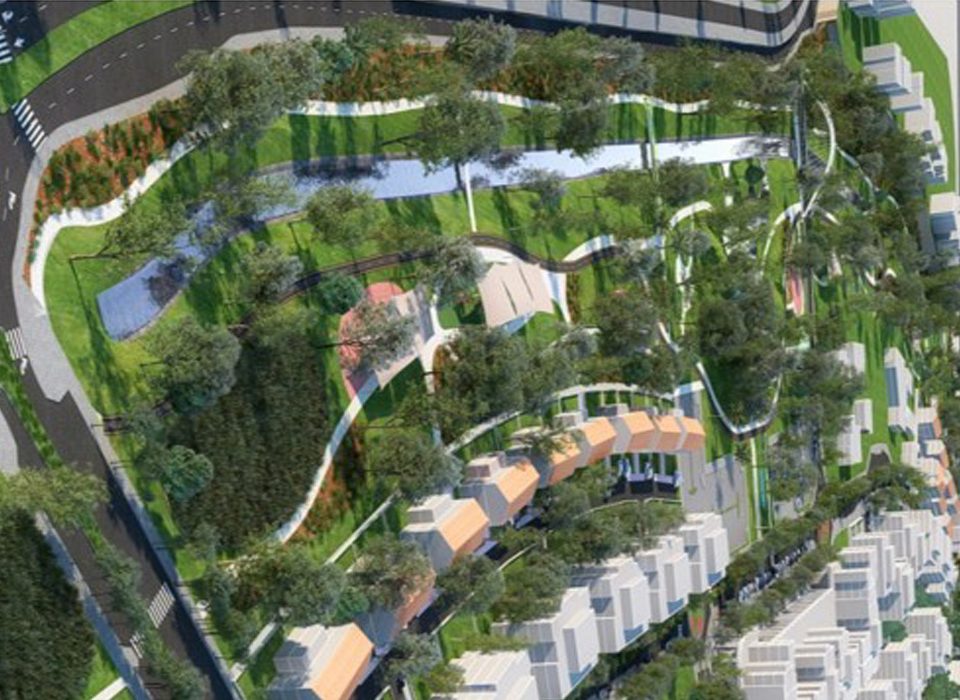
תפיסת התכנון של WAWA
16 בSeptember 2018

Green Building
Many years have passed since green building was considered the esoteric pursuit of madmen. It was the domain of ‘tree-huggers’ who understood, before anyone else, the problem of earth’s perishable resources, yet mistakenly believed that the solution lied in mud houses made of old tires (recycling, reducing the volume of waste( filled with straw (thermal insulation), that mimic the cool stone houses of Arab villages lying at the bottom of hills.
It is clear that a world populated by ten billion people, mostly living in dense areas, living together in large cities where they seek employment, culture, and other interests, would need something entirely different: high-density construction offering residences for all of these billions of people, while protecting agricultural land, forests, and open areas from unnecessary development.
At the same time, in recent decades, there has been a growing recognition in the world that we, human beings, actively endanger the continuation of life on earth as we know it.
Global warming, greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, melting icebergs, rising sea levels – these have all become household terms.
Ever since, in a rapid, impressive process, green building has evolved from the marginal pursuit of madmen to a concept that lies at the heart of building worldwide. The sophisticated core, using scientific methods, transforms the hi-tech world to the traditional low-tech, and is changing worldwide architecture for the first time since the modern architecture movement of the early twentieth century.
As a relatively new field, green building and architecture have many people asking: What is green building? In contemporary, advanced, prominent green building, there are many approaches with many emphases. The currently accepted, broad definition of green building is:
“Green building is a systemic, inclusive approach for planning, building, and operating buildings and the urban environment. The goal of green building is to create a healthy, comfortable living environment while avoiding harm to natural, perishable resources and the environment to the greatest possible extent. Green building can be seen in the use of environmentally friendly and recycled materials, and in planning that allows maximum savings of energy and water.”
That is the definition – but how can it be broken down?
What is a ‘green house?’ Who decides that it is green? How do you promote a planning and operational process for a green house? The fast, evolutionary process of the past 20-30 years of green building has introduced certifications that define green buildings, neighborhoods, and cities.
These include the British BREEAM certification, the leading American LEED certification that appeals to the whole world, the Australian Green Star, and the 5281 certification here in Israel – certification for sustainable building.
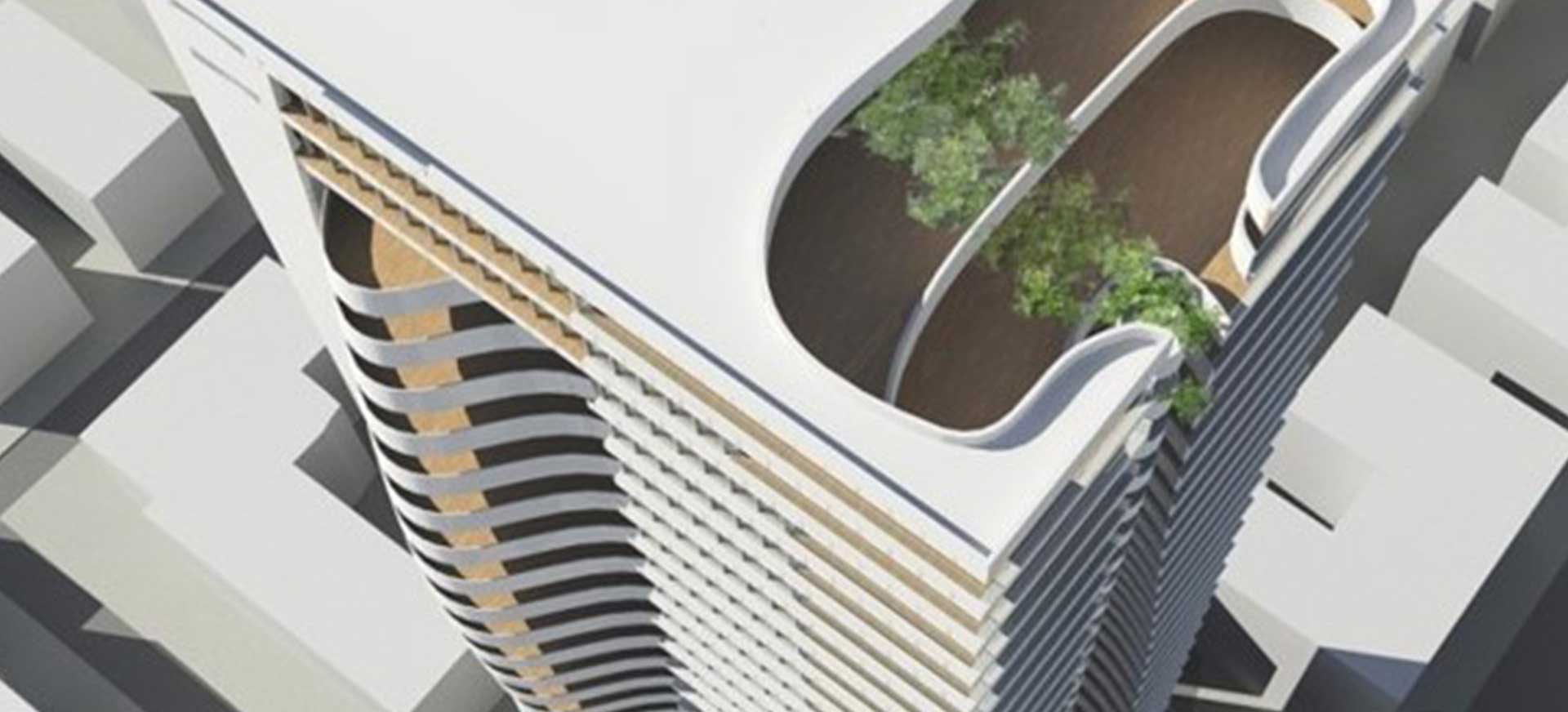

The certification is not the most important aspect, of course, but serves as a tool to guide and motivate, and is at times required by the local regulator. The United States, for example, requires all public structures to comply with the LEED certification, and in Israel, the Forum 15 decided that all large cities must comply with the 5281 green building certification and must be officially ‘green certified.’
As a rule, all certifications address a combination of components that make a house green: energy, water, materials, health, environment, and waste.
For example:
Energy conserved through proper planning that includes good insulation of the building’s exterior – walls and roofs, correct positioning of the building, long facades to the north and south, window positioning and size, natural ventilation requiring windows on opposing sides of the building, and the use of economical air conditioning and electrical appliances.
Once energy has been conserved, we create as much clean energy on the site as possible – PV, wind, geothermal, etc., thus minimizing the use of perishable resources.
At the same time, this results in considerable saving in energy.
Water is a perishable resource. In many regions it is scarce and is at times grounds for war. It is often polluted by ‘civilization’ – waste and industrial toxins infiltrating groundwater, etc.
Green building greatly emphasizes the preservation of this resource in a variety of ways:
Harvesting rainwater and air-conditioner condensation to be recycled and used for irrigation or for groundwater penetration, greywater purification conducted around the project area, and its use to flush toilets or for irrigation, etc.
Savings on consumption through the use of economical devices in bathrooms in combination with sensors, computerized systems for drip irrigation, the use of local, water-conserving vegetation, etc.
Green planning also addresses the types of materials in use, such as materials with green certification encouraging the use of local products (that do not require long-distance transportation, thus conserving energy and minimizing pollution, contributing to the local community through hiring locally, etc.), products containing recycled materials that do not contain toxic gases, etc.
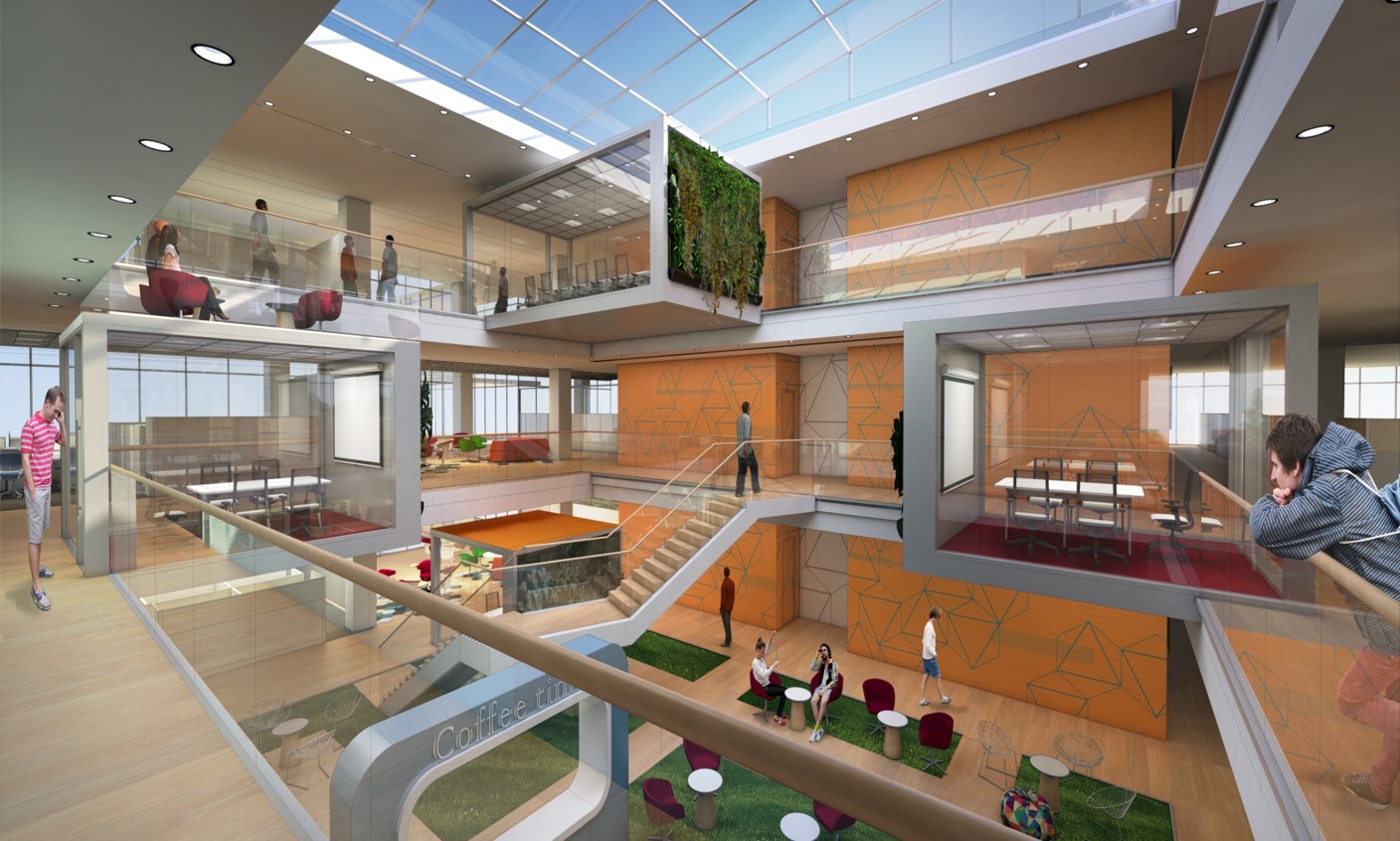
This focus expands to the concept of the human life environment (residences, work, studies, leisure), while respecting and preserving its natural surroundings. For example, office buildings and public buildings are required to provide direct access to scenery, lighting, and natural ventilation – components that have been empirically proven as offering a health advantage, and improving the accomplishments and efficiency of residents, students, and employees.
In terms of environmental aspects, we will use night fixtures that points downwards and is not a blinding light directed upwards to the sky, in order to minimize the urban phenomenon of light pollution and the disturbance of nocturnal birds. We will conduct an ecological survey to treat or transport bulbs, seeds, and local wildlife in an orderly fashion during construction, in order to return them to the environment once construction is completed, or in order to transport them to parallel environments.
This idea can be expanded upon, but the principle idea is clear.
Leading the green planning process requires the green building consultant to address various processes and parameters. The consultant simplifies the process, clarifying it for the developer or the planner. Correct green building consulting often prevents unnecessary costs, brings about high positioning of the project, and leads to higher profits for the developer, while adhering to planning and operational schedules.
It is not mandatory for the green building process to be enacted according to certification guidelines; what matters most, of course, is its concrete performance. Our experience has shown, however, that when working with green building certification guidelines, we avoid cutting corners (and avoid allowing the client to cut corners). Therefore, it is highly recommended to undergo the green building certification process.
One of the most impressive aspects of green building is that often, there is a sense that tasks performed are small and insignificant (such as harvesting roughly 40 liters of air-conditioner condensation per apartment per day). Yet, when we have one green house adjacent to another, and then another, from an urban perspective this adds up to a significant change (a continuation of the previous example where on the urban level, preservation can result in tens of thousands of cubic meters of water a day). A global perspective demonstrates that these changes hold exponential value, leading to a green house, a green neighborhood, a green city, and a green, sustainable world. This serves us as well as future generations to improve quality of life, health, achievements, and to reduce the cost of energy, water, waste disposal, etc. As a bonus, it saves the beauty and nature of our planet from destruction and environmental catastrophes.
Architect Yuval Shem-Or
WAWA Green Architecture